Cybersecurity threats are evolving, and Android devices are often the weakest link in digital security. Whether you’re a penetration tester securing networks or a researcher analyzing vulnerabilities, the right hacking tools can make all the difference.
But which tools are safe, legal, and effective? This guide explores the most trusted Android hacking applications, from penetration testing kits to network analyzers, helping you navigate the ethical and technical aspects of mobile security while avoiding unreliable or malicious software.
Criteria for Trustworthy Android Hacking Tools
Not all hacking tools are created equal—some are essential for ethical penetration testing, while others pose significant security risks. A trustworthy hacking tool must be open-source or backed by a reputable cybersecurity firm, ensuring transparency and eliminating hidden backdoors.
Frequent updates and active developer support are crucial, as outdated tools can introduce vulnerabilities rather than detect them.
Ethical hacking communities recognize tools like Kali NetHunter and Metasploit due to their widespread use in penetration testing certifications and security audits.
Conversely, tools with a history of stealing user data or being repackaged with malware should be avoided. A strong reputation among professionals, integration with leading security frameworks, and compliance with cybersecurity laws are key indicators of reliability.
Key Factors of Trustworthy Android Hacking Tools:
| Criteria | Importance | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Source | Ensures transparency and community support | Kali NetHunter, Termux |
| Frequent Updates | Reduces vulnerabilities and enhances security | Metasploit, Wireshark |
| Industry Recognition | Trusted by ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals | zANTI, Metasploit |
| Legal and Ethical Use | Complies with cybersecurity laws and guidelines | Kali NetHunter, Wireshark |
Next, we examine the best Android hacking tools that meet these stringent criteria.
Top Trusted Android Hacking Tools for Ethical Hackers
Ethical hacking relies on powerful yet responsible tools to uncover security vulnerabilities and strengthen Android security.
The best tools serve specialized purposes, from penetration testing and network analysis to stealth monitoring and real-time vulnerability assessments.
Below, we examine six of the most trusted Android hacking tools, used by cybersecurity professionals worldwide.
Comparison of Top Android Hacking Tools:
| Tool Name | Main Function | Root Access Required | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kali NetHunter | Penetration Testing | Yes | Advanced Ethical Hackers |
| zANTI | Network Vulnerability Testing | No | Security Analysts |
| Metasploit | Exploit Development | Yes | Cybersecurity Professionals |
| Wireshark | Network Packet Analysis | No | Network Administrators |
| Termux | Command-Line Scripting | No | Developers & Ethical Hackers |
Kali NetHunter: This mobile penetration testing platform, developed by the creators of Kali Linux, transforms Android devices into powerful hacking machines.
It supports advanced attacks such as Wi-Fi packet injection, keylogging, and Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, making it a go-to tool for ethical hackers.
Unlike other tools, NetHunter requires a rooted device for full functionality, but its seamless integration with Metasploit makes it indispensable for professionals.
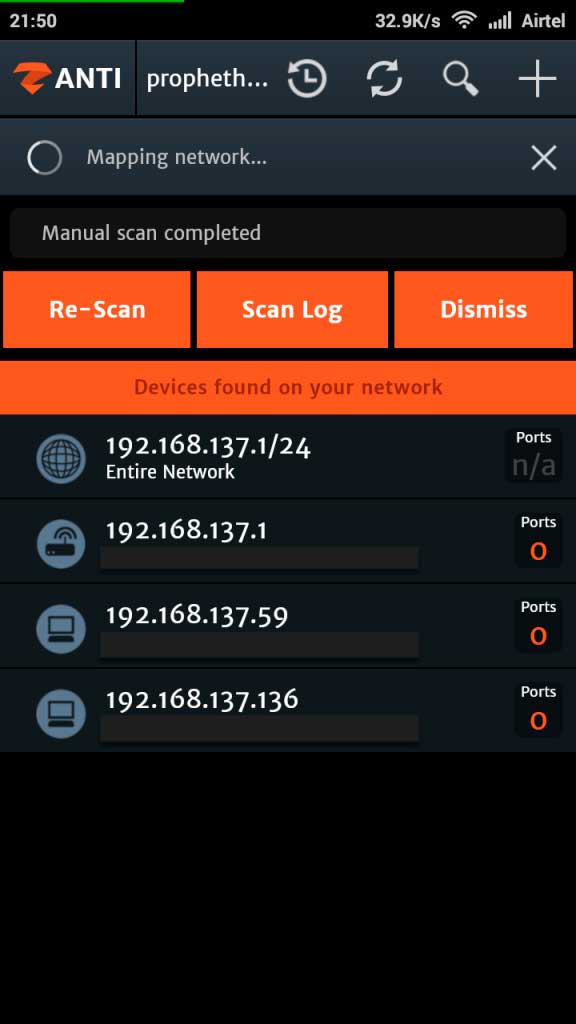
zANTI: A product from Zimperium, zANTI is a penetration testing toolkit designed for mobile security auditing. With a one-tap network vulnerability scan, it mimics cyberattacks to help IT administrators identify weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them.
One of its standout features is session hijacking, which can intercept and modify network traffic—an essential capability for testing Wi-Fi security. Unlike NetHunter, zANTI functions without root access, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
Metasploit Framework: One of the most widely used penetration testing tools, Metasploit allows security researchers to develop, test, and execute exploits against known vulnerabilities. The Android version is lighter than its desktop counterpart but remains a powerful tool for exploiting system weaknesses.
Ethical hackers use Metasploit for payload delivery, privilege escalation, and post-exploitation testing, ensuring that systems remain resilient against real-world attacks.
Wireshark: As a leading network protocol analyzer, Wireshark captures and inspects network traffic at a granular level.
It helps ethical hackers detect suspicious activity, analyze encrypted transmissions, and prevent data breaches. In real-world cybersecurity operations, Wireshark is invaluable for reverse-engineering malware attacks and tracking unauthorized data transfers, making it a core tool for penetration testers.
Termux: This Linux-based terminal emulator brings powerful command-line hacking tools to Android. Ethical hackers use Termux to run scripts, automate attacks, and execute network reconnaissance without requiring a full desktop environment.
With support for Nmap, Hydra, SQLmap, and even Metasploit, it acts as a portable penetration testing toolkit. Unlike most tools, Termux does not require root access, increasing its usability across various Android devices.
Hoverwatch: While not a traditional hacking tool, Hoverwatch is a stealth monitoring application used for security research, parental control, and employee tracking. It captures GPS locations, call logs, and social media messages, making it a valuable tool for ethical monitoring and forensic investigations.
However, its potential misuse raises legal and ethical concerns, emphasizing the importance of responsible deployment.
Each of these tools plays a unique role in penetration testing and security auditing, ensuring that ethical hackers can safeguard Android systems against cyber threats.
Next, we examine the implications of using these tools on rooted versus non-rooted Android devices and their impact on security.
Kali NetHunter
Kali NetHunter is a mobile penetration testing platform developed by Offensive Security, designed to bring the power of Kali Linux to Android devices.
It enables ethical hackers to conduct wireless network audits, password cracking, and remote exploits directly from their smartphones.
Unlike its desktop counterpart, NetHunter offers unique mobile capabilities such as Wi-Fi injection, HID (Human Interface Device) attacks, and NFC security testing, making it ideal for real-world security assessments. Root access is required for full functionality, but its ability to simulate sophisticated attacks makes it a staple for cybersecurity professionals.
For broader network analysis, tools like zANTI offer more user-friendly alternatives.
zANTI
zANTI, developed by Zimperium, is a mobile penetration testing toolkit designed to simulate real-world cyberattacks and uncover security vulnerabilities in Wi-Fi networks. It provides a one-tap network scan, allowing ethical hackers to identify weak encryption, open ports, and potential entry points.
One of its most powerful features is Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack simulation, which enables users to intercept and modify network traffic in real time.
With its intuitive interface, zANTI is an excellent choice for network mapping and vulnerability assessment, even for beginners.
While it excels in monitoring, tools like Metasploit take exploitation and advanced penetration testing to the next level.
Metasploit Framework
Metasploit Framework, developed by Rapid7, is one of the most powerful penetration testing tools used by ethical hackers to find and exploit vulnerabilities in Android applications and networks. It allows security professionals to deploy payloads, escalate privileges, and perform post-exploitation analysis on compromised systems.
While the desktop version supports a vast library of exploits, the Android-compatible edition focuses on mobile application security testing and remote device exploitation. Its advanced capabilities make it ideal for professional penetration testers rather than beginners.
For more detailed network traffic analysis and forensic investigation, experts often pair Metasploit with Wireshark, which specializes in real-time packet inspection.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a powerful network protocol analyzer widely used by cybersecurity professionals for packet sniffing and forensic analysis. Ethical hackers rely on it to detect security threats, analyze encrypted and unencrypted traffic, and troubleshoot network vulnerabilities.
For example, Wireshark can identify suspicious packets associated with Wi-Fi hacking attempts, such as rogue access points or unauthorized ARP spoofing attacks. By inspecting captured traffic in real time, security experts can pinpoint weaknesses in a network’s security posture and take corrective measures.
While Wireshark provides deep network visibility, command-line-based hacking tools like Termux offer greater flexibility for Android penetration testing and automation.
Termux
Termux is a Linux-based terminal emulator that turns an Android device into a powerful cybersecurity toolkit. Ethical hackers use it to run penetration testing scripts, automate security audits, and perform network diagnostics without requiring root access.
Its compatibility with Nmap (network scanning), Hydra (password cracking), and SQLmap (database exploitation) makes it a Swiss Army knife for mobile penetration testers. Unlike GUI-based tools, Termux provides full control over command-line hacking utilities, making it a favorite among professionals.
While it excels in automation and scripting, more specialized monitoring tools like Hoverwatch focus on real-time tracking and device surveillance.
Hoverwatch – A Remote Monitoring and Tracking Tool

Hoverwatch is a stealth monitoring tool designed for GPS tracking, call monitoring, message interception, and social media surveillance.
It runs silently in the background, capturing data from the target device without alerting the user.
While marketed for parental control and employee monitoring, its potential for misuse raises serious ethical and legal concerns.
Unlike ethical hacking tools like Wireshark or Metasploit, which focus on security testing, Hoverwatch leans toward surveillance rather than penetration testing.
Users must ensure compliance with privacy laws before deploying it. The next section explores the impact of using hacking tools on rooted versus non-rooted Android devices.
Considerations for Rooted vs. Non-Rooted Android Devices
Rooting an Android device unlocks deep system access, allowing hacking tools to operate at a higher privilege level.
This enables penetration testers to run powerful applications like Kali NetHunter, which requires root for advanced exploits such as Wi-Fi packet injection and HID attacks.
Rooted vs. Non-Rooted Android for Hacking Tools:
| Aspect | Rooted Android | Non-Rooted Android |
|---|---|---|
| Access Level | Full system access | Limited to user-space operations |
| Security Risk | Higher (prone to malware & exploits) | Lower (protected by Android security) |
| Tool Compatibility | Works with all hacking tools | Limited tool functionality |
| Best Use Case | Advanced penetration testing | Basic security audits |
However, rooting also introduces significant risks, including weakened security, loss of manufacturer support, and exposure to malware.
On the other hand, non-rooted Android devices provide a more secure and stable environment, but with limited access to system-level hacking functions.
Tools like zANTI function effectively without root privileges, enabling network vulnerability assessments and MITM attack simulations while maintaining device integrity. Similarly, Termux allows users to execute powerful penetration testing commands without modifying system files.
Choosing between rooted and non-rooted hacking tools depends on use case, risk tolerance, and security considerations. Ethical hackers must balance functionality with safety, ensuring they operate within legal and ethical boundaries.
The next section explores the legal and ethical implications of using hacking tools on Android devices.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Using Hacking Tools
The use of hacking tools walks a fine line between ethical cybersecurity practices and illegal activities. Ethical hackers and penetration testers use these tools to identify vulnerabilities, strengthen security, and protect digital assets, but unauthorized access to networks or data without explicit consent violates cybersecurity laws.
Legal Boundaries and Ethical Considerations:
| Legal Factor | Details | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration Testing | Legal with explicit permission | Ethical hackers testing company networks |
| Unauthorized Access | Illegal under most cybersecurity laws | Hacking into a private Wi-Fi network |
| Spyware Usage | Illegal if used without consent | Using Hoverwatch without user approval |
| Ethical Certifications | Required for professional penetration testers | CEH, OSCP |
The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the U. S.and similar international regulations criminalize hacking without permission, even if done with good intent.
To stay compliant, cybersecurity professionals must obtain explicit authorization before conducting security assessments.
Ethical hacking certifications, such as Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) or OSCP, enforce legal guidelines for responsible tool usage. Misuse of tools like Hoverwatch for unauthorized surveillance can result in severe legal consequences.
Understanding these legal and ethical constraints is crucial before engaging in penetration testing or digital forensics. The next section summarizes the key takeaways from this guide.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Android hacking tools requires balancing functionality, security, and legality. Ethical hackers rely on tools like Kali NetHunter, zANTI, Metasploit, and Wireshark for penetration testing and network security, while Termux offers command-line flexibility.
Monitoring tools like Hoverwatch raise ethical concerns, emphasizing the importance of responsible use. Whether on a rooted or non-rooted device, users must operate within legal boundaries to protect digital systems ethically.
Understanding these tools empowers cybersecurity professionals to enhance security, not compromise it.